Char Dham Yatra
Context:
- Since the beginning of the Char Dham Yatra of this year which started on May 3, around twenty three pilgrims have lost their lives on their pilgrimage.
- Mainly due to cardiac related issues like heart attack, hypertension and other comorbities, a majority of them are above sixty years of age.
About the Yatra:
- The Char Dham mentioned in the above context is also referred to as chota chardham, which includes Yamunotri, Gangotri, Kedarnath and Badrinath.
1) Yamunotri – This Shrine is dedicated to River Yamuna.
2) Gangotri – This shrine is dedicated to goddess Ganges.
3) Kedarnath – This temple is dedicated to Lord Shiva in the form of Kedar.
4) Badrinath – This temple is dedicated to Lord Vishnu in the form of Badrinath. - The Char Dham means the four dhams is a set of four pilgrimage sites which is very auspici.ous in the Hindu belief.
- In the Hindu sect, it is believed that a person visiting all the four sites will attain Moksha ( Salvation)
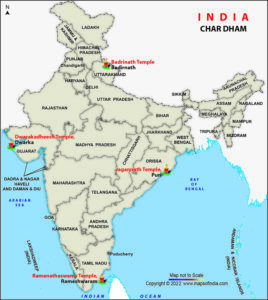
The four dhams as described by Adi Shankaracharya includes:
1. Badrinath – located on the banks of the river Alkananda in Uttarkhand, the town lies between the Nar and Narayan mountain ranges
2. Dwarka – located in the confluence of the river Gomti merging into Arabian sea in the state of Gujarat.
3. Puri – located in the state of Odisha, here the deity is Krishna, who is worshipped as Jagannatha
4. Rameswaram – located in Tamil Nadu where lord shiva is worshipped.

Issues associated:
- The four holy sites located in Uttarkhand are located on high altitudes in the Himalayas.
- The pilgrims who visit these sites are prone to sudden low temperatures, low humidity, low air pressure, low oxygen levels and increased ultraviolet radiation.
- Due to limited public transport facilities many pilgrims choose to walk who are prone to above mentioned threats.
- The air at the ground level comprises different molecules with nitrogen 78% and oxygen 21% .
- With increase in the altitude number of oxygen molecules in a given volume of air changes.
- At higher altitudes the partial pressure of oxygen changes and the oxygen molecules are further put apart because of less air pressure.
- This leads to less amount of oxygen molecules in the same amount of air we breathe.
Source: THE HINDU.
For more update, click here to join our telegram channel




