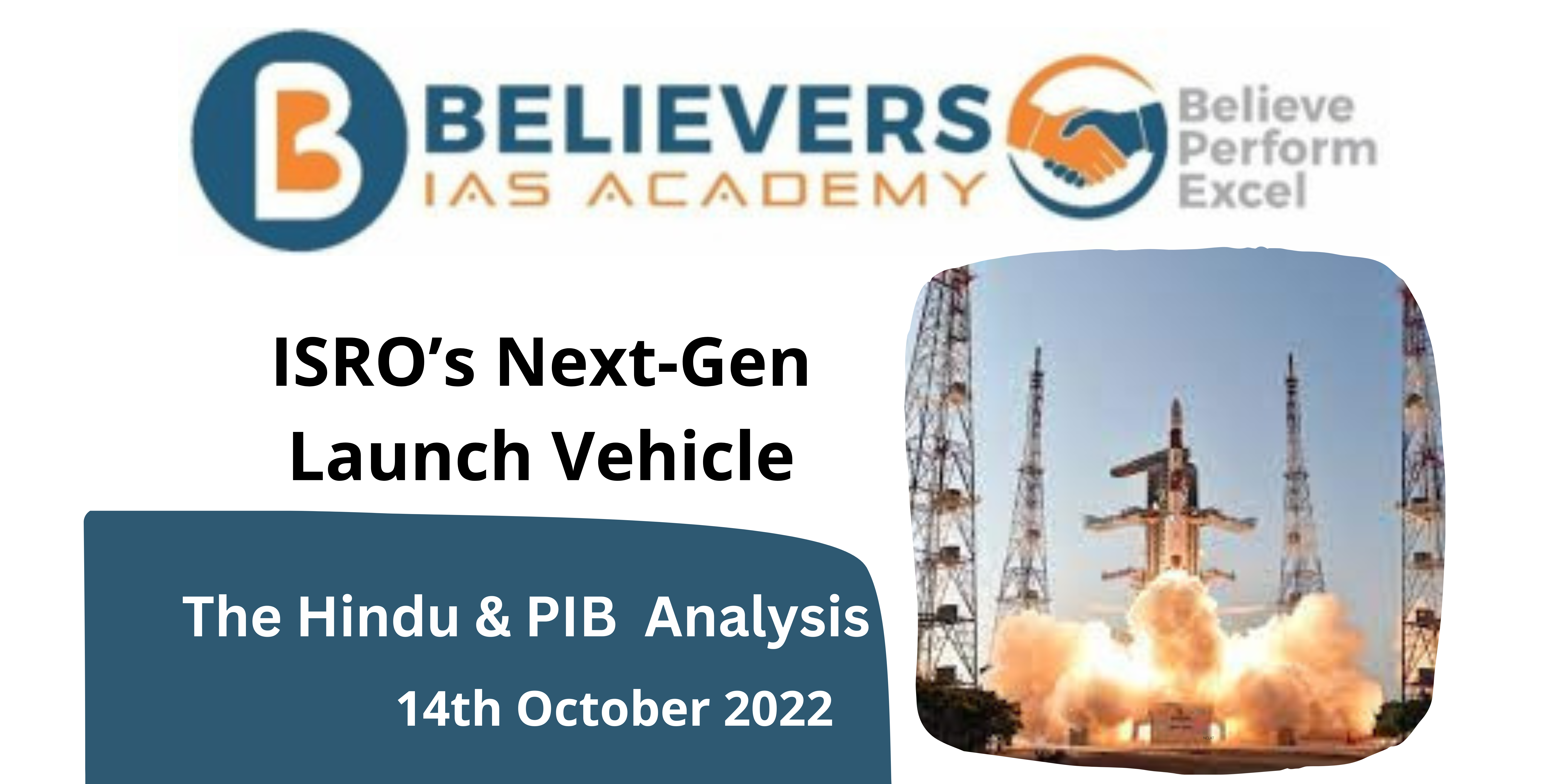
ISRO’s Next-Gen Launch Vehicle
#GS-03 Science and Technology
For Prelims
About Next-Gen Launch Vehicle:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is developing a Next-Gen Launch Vehicle (NGLV), which is expected to replace the current operational systems like the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV).
- NGLV is aimed to be a cost-efficient, three-stage, reusable heavy-lift vehicle with a payload capability of 10 tonnes to Geostationary Transfer Orbit.
- NGLV will feature semi-cryogenic propulsion for the booster stages which will be cheaper and efficient.
- The Low Earth Orbit (LEO) payload capability will be twice that of the Geostationary Transfer Orbit i.e., 20 tonnes.
- However, payload capability will be lower when the rocket is reusable.
Current Launch vehicles of ISRO:
About PSLV:
- Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) is the third generation launch vehicle of India.
- It is the first Indian launch vehicle to be equipped with liquid stages.
- It is a four stage launch vehicle.
- A large solid rocket motor forming the first stage,
- An earth storable liquid stage as the second stage,
- A high-performance solid rocket motor as third stage, and
- A liquid stage with engines as fourth stage.
- The vehicle successfully launched two spacecraft – Chandrayaan-1 in 2008 and Mars Orbiter Spacecraft in 2013.
- Since 1994 till 2017, PSLV has launched 48 Indian satellites and 209 satellites for customers from abroad.
About GSLV:
- The Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) project began in 1990 with the aim of acquiring an Indian launch capability for geosynchronous satellites.
- GSLV is a fourth generation launch vehicle and is a three stage vehicle with four liquid strap-ons and the indigenously developed cryogenic Upper Stage (CUS) powers its third stage.
GSLV Mk III
- GSLV Mk III is a three-stage heavy lift launch vehicle developed by ISRO.
- The vehicle has two solid strap-ons, a core liquid booster and a cryogenic upper stage.
- GSLV Mk III is designed to carry 4 ton class of satellites into Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) or about 10 tons to Low Earth Orbit (LEO), which is about twice the capability of the GSLV Mk II.
- The first developmental flight of GSLV Mk III, the GSLV-Mk III-D1 successfully placed GSAT-19 satellite to a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) on June 05, 2017 from SDSC SHAR, Sriharikota.
- GSLV MkIII-D2, the second developmental flight of GSLV MkIII successfully launched GSAT-29, a high throughput communication satellite on November 14, 2018 from Satish Dhawan Space Centre SHAR, Sriharikota.
- GSLV MkIII-M1, successfully injected Chandrayaan-2, India’s second Lunar Mission, in to Earth Parking Orbit on July 22, 2019 from Satish Dhawan Space Centre SHAR, Sriharikota.