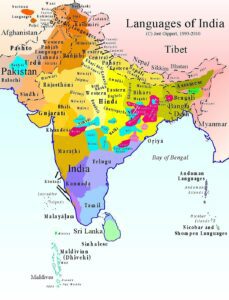
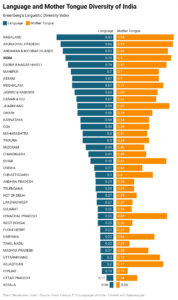
Language Policy in India
Context:
• The Governor of Tamil Nadu has recently asserted that the Central government did not impose Hindi or any other language on Tamil Nadu at the 37th convocation of Bharathiar University.
What are the Constitutional Provisions regarding language?
• Article 29 The Article states that any section of the citizens who have a “distinct language, script or culture of its own shall have the right to conserve the same.”
• Article 343 – it is to be Hindi in Devnagri script would be the official language of the Union of India, it also states that English will continue to be used as an official language for 15 years from the commencement of the Constitution.
• Even after the prescribed 15 years, the parliament through legislations can provide for use of English Language.
• The Official Language Act of 1963 provides for continued use of English without prescribing any time limit.
What are the provisions for the state?
• The constitution provides for legislature of a state to adopt any one or more languages in use in the state or Hindi as the official language of that state.
• Until that English is to continue as official language of that state.
• The act also lays down that English should be used for the purposes of communication b/w the Union and the non- Hindi states.
What are the provisions for the Judiciary?
• Article 348 (1) of the Constitution of India provides that all proceedings in the Supreme Court and in every High court shall be in English Language until Parliament by law otherwise provides.
• Under Article 348 (2), the Governor of the State may, with the previous consent of the President, authorize the use of the Hindi language or any other language used for any official purpose of the State, in the proceedings of the High Court having its principal seat in that State provided that decrees, judgments or orders passed by such High Courts shall be in English.
What does the constitution say about the Development of Hindi Language?
• The constitution imposes a duty upon the centre to promote the spread and development of the Hindi Language so that it may become the lingua franca of the composite culture of India.
Source: THE HINDU.
For more update, click here to join our telegram channel




